Android dev setup
Download and install JDK
Download
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk7-downloads-1880260.html
Select lastest version and download: jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz
Extract downloaded package into /opt/java
tar -xzvf jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /opt/java
Add jdk install dir to bashrc
export JDK_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.7.0_79
export PATH=$JDK_HOME/bin:$PATH
Download and install Android Studio
Download
http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
Select All Android Studio Packages: android-studio-ide-141.2456560-linux.zip
Extract downloaded package into work/android/tools
Add Android studion home into bashrc
export ANDROID_STUDIO_HOME=/home/dvn000/work/android/tools/android-studio
export PATH=$ANDROID_STUDIO_HOME/bin:$PATH Solve IBus issue
https://youtrack.jetbrains.com/issue/IDEA-78860
export IBUS_ENABLE_SYNC_MODE=1
Configuring VM Acceleration on Linux
http://blog.whitehorses.nl/2015/03/07/enabling-hardware-acceleration-for-android-sdk-emulator-on-linux/
http://developer.android.com/tools/devices/emulator.html#vm-linux
Adding SDK Packages
http://developer.android.com/sdk/installing/adding-packages.html
Run Android Studio add alias to bash alias androidstu=’studio.sh &’
About Android Studio
Features:
- Gradle-based build support (Like Apache Ant on ADT, task is same as make with Makefile in linux).
- Android-specific refactoring and quick fixes.
- Lint tools to catch performance, usability, version compatibility and other problems.
- ProGuard integration and app-signing capabilities.
- Template-based wizards to create common Android designs and components.
- A rich layout editor that allows users to drag-and-drop UI components, option to preview layouts on multiple screen configurations.
- Support for building Android Wear apps
- Built-in support for Google Cloud Platform, enabling integration with Google Cloud Messaging and App Engine.
(Src: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Android_Studio)
Q/A ?????
Android version vs API level?
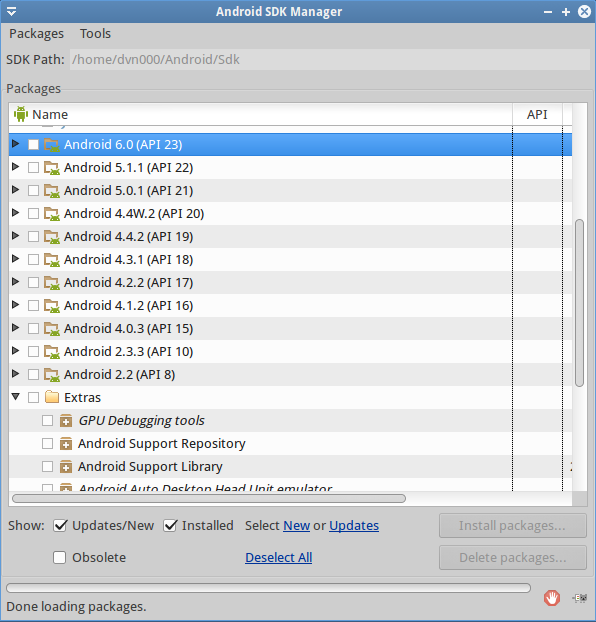
- API is for development (for developer), so the changes in new API level are more “inside”. But new version of Android usually adds more features for users, that are “visible” to user.
- This page http://developer.android.com/guide/appendix/api-levels.html , there is a table that shows relations between versions and API levels.
Android vs Intel vs Google System Image?
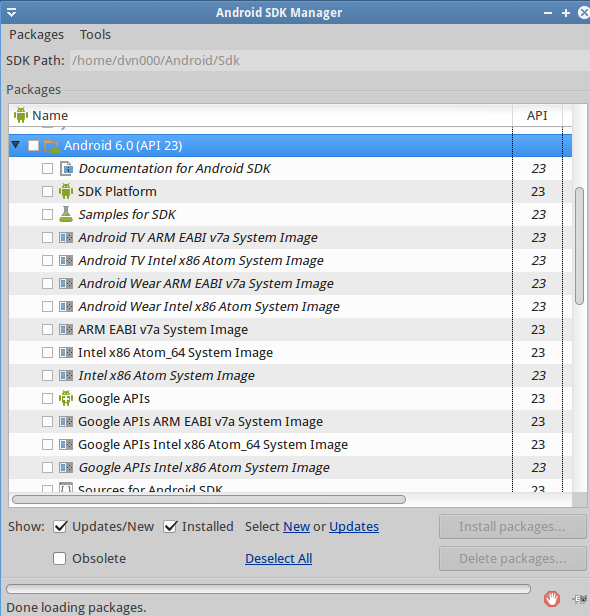
-
Android system image: In the beginning the only Android system images available ran on the ARM instruction set (for processor in real mobile). A system image is used to create different Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) and emulate the different Android devices in common use.
-
Intel system image: As developer workstations are usually Intel x86 based, the ARM instruction set had to be emulated as well. This resulted in poor performance from the AVDs due mainly to the amount of translation the x86 processor was doing to also emulate the ARM instruction set ==» At Android 4.0.3 (API 15) Intel provided their own x86 based Android system image. This could then be used to create AVDs that did not need to do ARM translation. Combined with the Intel Hardware Accelerated Execution Manager (HAXM) the x86 AVMs were up to 10 times faster than the equivalent ARM emulators.
-
Google API system image: Support for Google specific Android APIs like the Android Google maps API, are not provided with the standard Android system images. They need to be installed separately using the Android SDK Manager. To use these APIs with an x86 system image you need to also install the Google APIs (x86 System Image) for the same API level.
==> Should use Google API Intel x86 Atom_64 (for 64bit workstation) or Google API Intel x86 (for 32bit workstation)